Your greatest security threat may sit three desks away
By Jeff Copeland

These hackers aren’t trying to break down your firewall—they’re already inside, brewing coffee in your break room. While you’re fortifying defenses against external attacks, an insidious danger comes from those you trust most: your employees, contractors, vendors, and now, your AI systems.
Welcome to the new reality of cybersecurity, where 83% of IT and security professionals in the 2024 Cybersecurity Insiders survey reported at least one insider attack in the past year and 51% experienced six or more attacks.
The Enemy Within: What Insider Threats Really Look Like
An insider threat isn’t just the disgruntled employee plotting revenge. It’s anyone with legitimate access who—intentionally or accidentally—puts your organization at risk. Think of it as death by a thousand cuts, where each authorized login could be the one that brings you down.
Some notorious examples of insider threat activity:
- Tesla’s 2018 sabotage showed that one disaffected IT employee could disrupt an entire production line
- The ChatGPT data dumps at Samsung showed how well-meaning employees can accidentally reveal trade secrets by using AI platforms
- Crypto exchange Coinbase was hit with a ransomware demand after criminals bribed overseas customer-service contractors
- Apple accused a former employee of stealing secrets about its VisionPro headset, and handing them over to his new employer
Today’s insider threats aren’t just human—they’re algorithmic, automated, and evolving faster than traditional security can keep up.
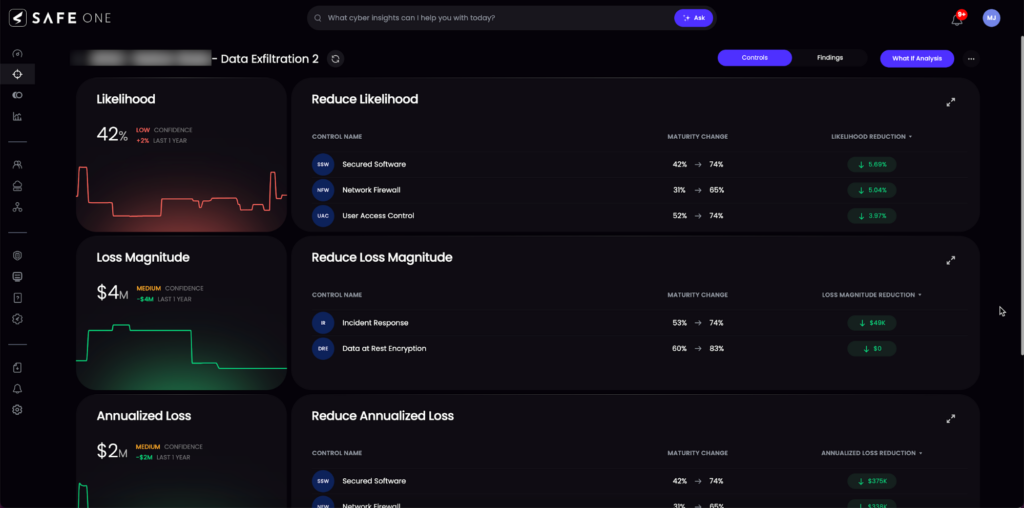
Gaming out approaches to mitigate risk of data exfiltration with the SAFE platform
The Five Faces of Insider Threats
- Malicious Insider: The Saboteur
The classic villain: employees who deliberately weaponize their access. They’re motivated by revenge, money, or ideology, and they know exactly where your vulnerabilities lie.
- Non-malicious Insider: The Accident Waiting to Happen
These are your good people making bad choices. They click suspicious links, use weak passwords, or inadvertently share sensitive data. “Shadow AI” users fall into this category—employees running unauthorized AI tools because they make life easier.
- Compromised Insider: The Unwitting Accomplice
Your employees whose credentials have been stolen without their knowledge through phishing or other forms of social engineering.
- Third Parties: The Trojan Horse
Third-party vendors, contractors, and partners who bring risk through the front door. The 2023 MoveIT breach, where the Cl0p ransomware gang exploited a file-transfer service, affected 2,700 organizations in one fell swoop.
- Artificial Intelligence as a Vector: The Digital Wildcard
AI systems that create new attack vectors. Poorly secured LLMs, misconfigured enterprise AI, or employees using AI to bypass security protocols represent the newest frontier of insider risk.
Insider Threat Red Flags that Demand Attention
Smart organizations don’t wait for breaches—they watch for warning signs. Here’s what to monitor:
Behavioral Red Flags
- Access creep: Employees viewing files far outside their job scope
- Data hoarding: Unusual downloads, especially to personal devices
- Permission pushing: Repeatedly testing system boundaries
- Attitude shifts: Vocal complaints about management or company direction
- Financial stress signals: Sudden lifestyle changes that suggest money troubles
Technical Red Flags
- Ghost logins: System access during off-hours or from unknown devices
- Breach attempts: Failed login attempts on restricted systems
- Data spikes: Sudden increases in file transfers or downloads
- Rogue devices: Unauthorized hardware or software connections
Situational Red Flags
- Workplace friction: Employees feeling undervalued or passed over
- Financial pressure: Personal circumstances that create desperation
- Security clearance changes: Revoked or downgraded access privileges
- Transition periods: Recent terminations, demotions, or role changes
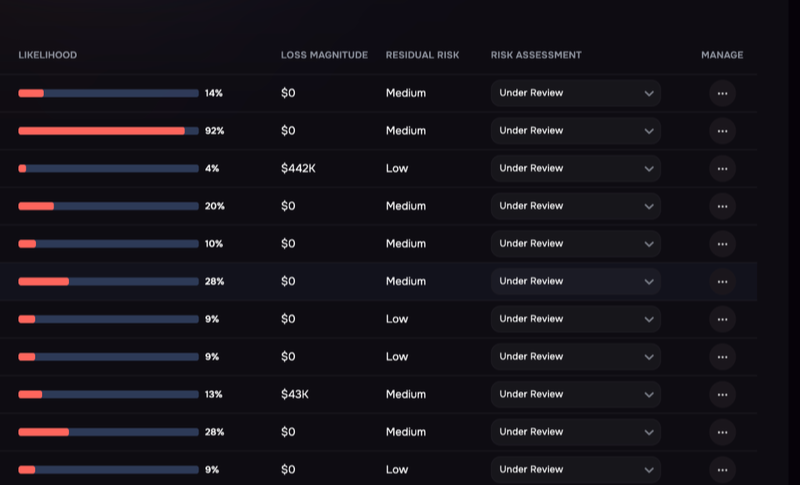
Assessing third parties for risk with the SAFE One platform.
The Vendor Vulnerability
Your third-party partners aren’t just service providers—they’re potential security liabilities. With 45% of businesses (in a Gartner survey) experiencing disruptions due to third-party failures, vendor management has become a critical security function.
Smart Vendor Risk Management:
- Rigorous onboarding: Automated intake processes and contract analysis
- Tiered risk assessment: Categorize vendors by potential impact
- Continuous monitoring: Real-time alerts for vendor security incidents
- Compliance tracking: AI-driven reporting for regulatory requirements
- Proactive offboarding: Identify and eliminate residual risks
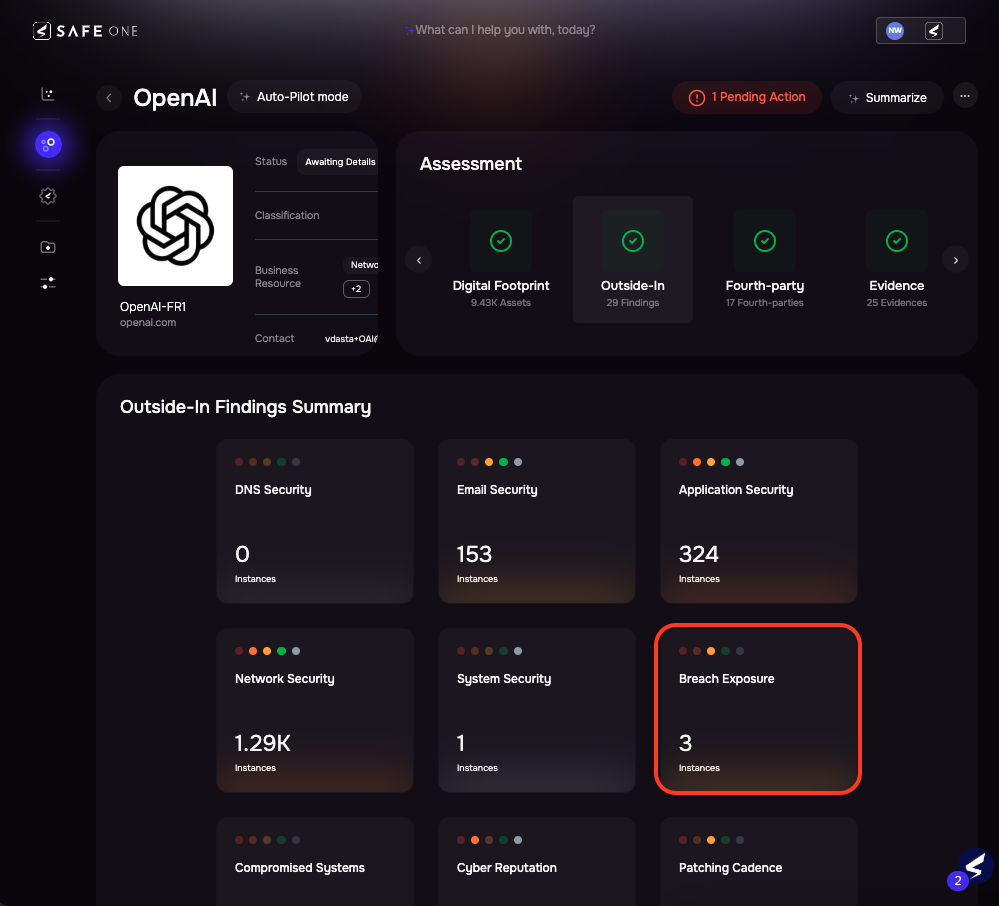
Assessing risk from an AI services vendor with SAFE.
Lean more about vendor risk management with SAFE.
AI: The Double-Edged Sword
Artificial intelligence promises efficiency but delivers complexity. Every AI implementation creates new attack surfaces and insider risks.
The New AI Threat Landscape
Shadow GenAI: Employees leak sensitive data through public AI platforms like ChatGPT, often without realizing the implications.
Foundational risks: AI models trained on inappropriate data create legal and reputational landmines.
Vendor vulnerabilities: Third-party AI providers with weak security protocols compromise your data by association.
Weaponized AI: Adversaries use AI to craft sophisticated social engineering attacks that traditional defenses can’t detect.
Quantify to Clarify: The FAIR Approach to Insider Risk
Here’s where insider threat management gets strategic: you can actually calculate the financial impact of these risks using the FAIR (Factor Analysis of Information Risk) model. Instead of vague “high, medium, low” assessments, FAIR helps you determine the probability of occurrence and financial impact for any insider threat scenario.
Real-World Risk Calculations: Sample FAIR Insider Risk Analysis
- Shadow GenAI scenario: 5% probability of sensitive data leakage through unauthorized AI usage, with a $5 million potential impact. Key risk driver: employees with both AI access exceptions and sensitive data privileges.
- Disgruntled employee scenario: 12% probability of data sabotage during layoff periods, with a $2.3 million potential impact. Key risk driver: employees with administrative access who receive termination notices.
- Vendor compromise scenario: 8% probability of third-party credential abuse, with a $7.2 million potential impact. Key risk driver: vendors with excessive system privileges and weak security controls.
- Negligent insider scenario: 25% probability of accidental data exposure through misconfigured systems, with a $1.8 million potential impact. Key risk driver: employees with configuration rights but inadequate training.
This approach transforms insider threat management from reactive firefighting into proactive risk investment decisions. When you can demonstrate that investing $200,000 in monitoring tools could prevent a $5 million breach, the business case becomes crystal clear. Learn more.
Operationalizing Insider Threat Defense with MITRE Techniques + FAIR
Organizations need a structured way to defend against insider threats. The MITRE Insider Threat TTP Knowledge Base extends MITRE ATT&CK® to insider risks, helping security teams map behaviors to real-world tactics and build stronger defenses.
Key benefits:
- Codifies insider behaviors into detectable patterns (e.g., data exfiltration, privilege abuse)
- Aligns technical indicators with MITRE techniques for better detection
- Supports threat hunting, detection engineering, and AI governance
- Enhances FAIR-based risk quantification for more precise risk analysis
Using MITRE insider TTPs with FAIR makes insider risk programs proactive, targeted, measurable, and adaptable. The SAFE Threat center uses FAIR analysis to generate automated insights into risk scenarios based on your vulnerabilities. Learn more about threat modeling with SAFE.
Insider Risk: Your Defense Arsenal
User & Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA)
Think of this as your organizational sixth sense—monitoring both human and AI behaviors for anomalies that signal trouble.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Extended monitoring that shuts down unauthorized data outputs before they become data leaks.
Privileged Access Management (PAM)
Strict controls over who can access what, when, and why—including AI systems.
Zero Trust Architecture
“Never trust, always verify” becomes your mantra, with continuous validation of every user and device, including AI applications.
Build Your Insider Defense Strategy in Five Layers
Layer 1: Education – Create awareness programs that address modern insider risks, not just traditional threats.
Layer 2: Monitoring – Implement comprehensive surveillance covering behavioral, technical, and situational indicators.
Layer 3: Governance – Establish clear policies for AI usage by insiders and for third-party access that evolve with emerging threats.
Layer 4: Assessment – Conduct regular risk reviews that account for new third-party vulnerabilities.
Layer 5: Contracts – Enforce stringent security requirements in all third-party agreements.
The Future of Insider Threat Defense
The security landscape has fundamentally shifted. Insider threats now encompass human psychology, technical vulnerabilities, third-party risks, and AI complexities. Organizations that recognize this evolution—and adapt accordingly—will thrive. Those that don’t will become cautionary tales.
Your defense strategy must be as sophisticated as the threats you face. Start with robust detection tools, strengthen your governance frameworks, and extend your vigilance to AI-driven risks.
The future of cybersecurity isn’t about building higher walls—it’s about knowing who’s already inside.
Ready to strengthen your defenses? For cutting-edge solutions, consider the SAFE TPRM platform that addresses insider threats, third-party breaches, and AI risks in one integrated approach.


