“Effective CISOs frame cyber threats as business risks, not purely technical challenges,” influential report says.
By Wes Hendren
The tide of our digital evolution is cresting higher than ever before. With each new technological stride, our reliance on interconnected networks grows. And as the World Economic Forum (WEF) Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025 makes crystal clear: cyber risks are no longer confined to backroom IT issues. They’ve taken center stage in boardrooms, C-suites and even the headlines. This isn’t just a story about risks—it’s about the profound opportunities that lie in mastering this digital revolution.

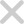
The Complexity Conundrum
As seen by the WEF, the cyber landscape of 2025 is marked by converging forces that magnify risks while challenging traditional defenses. These forces include:
- Geopolitical Tensions: Cyberattacks mirror global unrest, with state-sponsored threats targeting economies, infrastructure, and societal trust.
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: Modern supply chains, vast and opaque, amplify risks where a single failure can cascade into systemic collapse.
- Emerging Technologies: AI and quantum computing unlock innovation, but expose organizations to sophisticated, unforeseen vulnerabilities.
- Regulatory Fragmentation: A web of overlapping mandates complicates compliance, particularly for organizations operating across borders.
- Skills Gaps: The shortage of cyber talent leaves many organizations ill-equipped to counter the growing threat landscape.
These dynamics deepen the divide between large, resource-rich enterprises and smaller, under-staffed organizations, underscoring the urgency of collaboration and innovation.
WEF Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025
AI: The Crossroads of Opportunity and Risk
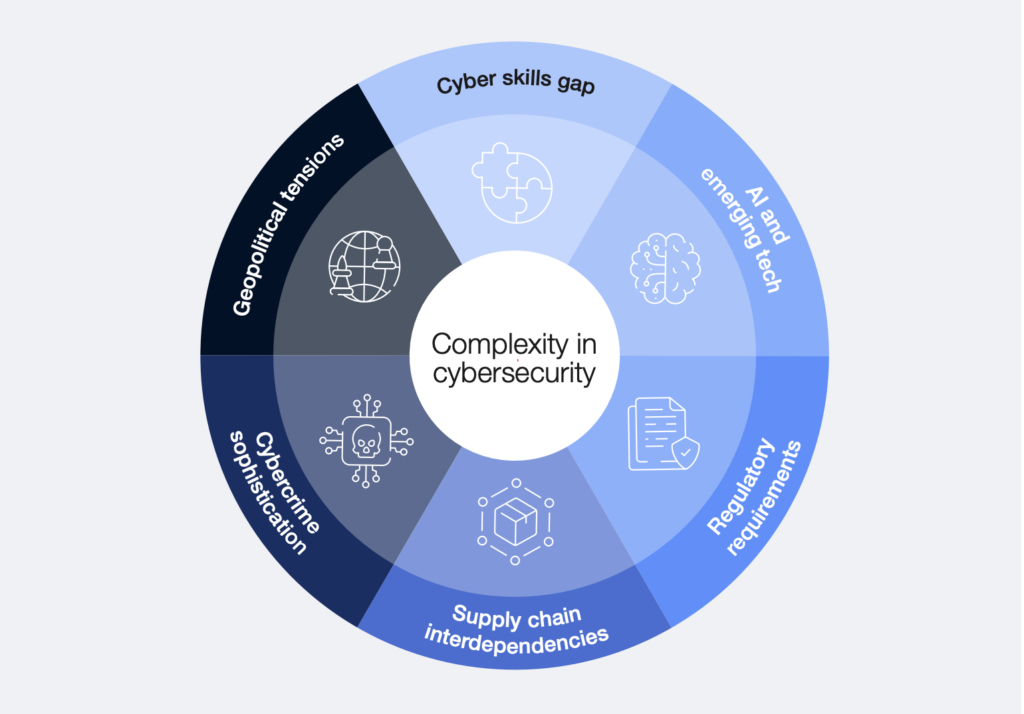
On one side, generative AI (GenAI) powers cyber resilience by enabling predictive threat detection, automating responses, and optimizing defense strategies. Yet, it also empowers adversaries, enabling sophisticated phishing campaigns, deepfake fraud, and ransomware at unprecedented scales.The paradox is stark: while 66% of organizations surveyed by the WEF recognize AI’s transformative impact, only 37% have safeguards in place to ensure its secure deployment. Without a culture of intentional and secure implementation, the risks of AI may outpace its benefits.
Supply Chains: The Achilles’ Heel of Cyber
Supply chains are the arteries of global commerce—but their complexity makes them a prime target for cyberattacks. 54% of large organizations surveyed identify third-party risks as their biggest barrier to achieving cyber resilience. With limited visibility into supplier networks and inconsistent enforcement of security standards, vulnerabilities multiply.
Resilience lies in transparency. By adopting standardized practices, leveraging threat intelligence, and embracing collaborative strategies, organizations can mitigate risks while preserving the interconnected benefits of global supply chains.
World Economic Forum Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025 survey results
The Rise of the CISO and the Boardroom Imperative
In the golden age of digital disruption, Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) have assumed a pivotal role. According to the WEF’s 2024 Annual Meeting on Cybersecurity, 60% of CISOs meet with their boards three to four times a year, presenting cyber risk not as a backend inconvenience but as a strategic business risk.
“Effective CISOs frame cyberthreats as business risks rather than purely technical challenges,” the WEF writes. “By contextualizing cyber incidents in terms of business continuity, reputation and financial impact, they enable CEOs and boards to view cybersecurity as part of the broader risk landscape…
“CISOs now quantify cyber risk by its effects on market share, brand trust, safety and regulatory compliance, showing how cyber incidents can ripple throughout an organization.”
Key Takeaways
- Translating Tech to Business: CISOs who speak the language of the balance sheet – quantifying how cybersecurity (or the lack thereof) influences financial losses, regulatory compliance, and brand trust – are earning the ears of executives.
- Direct Line to the CEO: Roughly 24% of CISOs now report straight to the chief executive, underscoring how deeply cybersecurity is woven into modern business strategy.
In an age of hyperconnectivity, CISOs serve as navigators, helping boards steer through an ocean of new threats. Their insights aren’t just about firewalls or patch updates; they’re about safeguarding competitive advantage and ensuring organizational longevity in a volatile digital ecosystem.
The Ever-Widening Economic Ripples of Cyberattacks
As the WEF report points out, cybercrime doesn’t just target specific organizations – it’s increasingly shaping the global economy. From critical infrastructure hacks to organized cybercrime syndicates, the digital battlefield impacts market share, shareholder value, and public trust.
Bigger Picture Impacts
- $12.5 Billion in 2023: The FBI tallied an excess of $12.5 billion lost to cybercrime last year alone, a figure that continues to climb.
- Cyber Insurance Premiums: As attack frequency escalates, so do insurance costs, placing additional pressure on enterprises, especially SMEs.
In our interconnected world, a single breach can swiftly spiral into a nationwide or worldwide crisis, underscoring cybersecurity’s status as a shared, systemic challenge rather than a solitary corporate concern.
Cyber Resilience: A Strategy, Not an Afterthought
Just as climate change has prompted nations to deploy incentives for sustainable energy, many experts argue that we need similar incentives in the cybersecurity arena. Think of it as “renewable security”: a sustainable, long-term strategy to ward off malicious actors and stabilize economies.
Parallels with Climate Action
- Government Incentives: Subsidizing cybersecurity solutions for SMEs could drive faster adoption of crucial defenses like multifactor authentication and security-awareness training.
- Long-Term Vision: Proactive security measures cost far less than the devastating financial fallout of a massive data breach, particularly for smaller firms operating on narrow margins.
By forging a whole-of-system approach – akin to global climate initiatives – policymakers can bolster the front lines of cyber defense across all sectors, ensuring no organization is left behind due to budget constraints.
World Economic Forum Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025 survey results
Quantifying Cyber Risk: The Next Frontier
“All of these factors point to the need for leaders to quantify cyber risks and their economic impacts to align investments with core business objectives,” the WEF report states. We can’t effectively manage what we can’t measure. And while 60% of surveyed CEOs and CISOs say cyber-risk management is now integrated into overall enterprise risk management, fewer than half feel their organizations are investing enough.
Why Measuring Matters
- Accurate Budgeting: Assigning real-world costs to potential breaches makes it clear how investments in cybersecurity protect the bottom line.
- Leadership Buy-In: When leaders see tangible numbers tied to reputational or financial damage, they’re more likely to greenlight budget requests that reinforce defense.
- Future-Proofing: Data-driven insights help organizations anticipate emerging threats, rather than merely reacting to the latest crisis.
The complexity of constantly shifting attack vectors has left many executives struggling to identify the “right” level of cybersecurity spending. Yet ignoring these realities is a high-stakes gamble no organization can afford.
The Cyber Workforce as an Economic Engine
A thriving cybersecurity workforce is more than a talent pipeline—it’s an economic catalyst. New job opportunities, from threat analysts to incident responders, provide stable, well-paying careers that boost local and global economies.
Benefits of a Skilled Cyber Workforce
- Economic Uplift: Cyber professionals often enjoy competitive salaries, fueling consumer spending and local growth.
- Innovation Multiplier: Skilled workers drive research and development across industries, fostering the next wave of technological breakthroughs.
- Diversity and Inclusion: Cybersecurity demands varied skill sets, opening doors for professionals from all backgrounds and disciplines to enter a lucrative field.
We are witnessing the birth of an economic powerhouse as cybersecurity roles expand and organizations vie for top talent. This synergy between economic development and digital defense is a hallmark of our new, networked civilization.
A Call to Action: Building a Cyber-Resilient Culture
In a world where technology is advancing at an exponential pace, cyber risk is a certainty. The question is how effectively we choose to manage it. The WEF’s Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025 underscores that proactive, integrated, and forward-thinking approaches are our best bet.
Leadership Priorities
- CISO Empowerment: Elevate cybersecurity leadership to the top levels, ensuring alignment with corporate strategy.
- Incentivize Best Practices: Governments and industry bodies must offer incentives—like subsidies or tax breaks—to SMEs and beyond.
- Quantify to Justify: Robust risk models, real-time analytics, and financial metrics help make cybersecurity a C-suite priority.
- Champion a Security Culture: From the boardroom to the break room, let cyber-resilience be everyone’s responsibility.
Much like the unstoppable wave of digital transformation, cyber resilience is an imperative of our time. By embracing it, we’re not merely safeguarding intellectual property or preventing downtime – we’re fostering a culture that supports continuous innovation and long-term economic vitality.
Parting Thoughts on the World Economic Forum Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025
The future will continue to enthrall us with ever more connected systems, quantum leaps in AI, and expansions in the digital frontier. Cyber resilience is the navigational compass, ensuring these possibilities remain opportunities rather than pitfalls. As we stand at the brink of a revolution shaped by ones and zeros, let’s heed the data, embrace the CISO’s counsel, and step boldly into a safer, more innovative tomorrow
When technology is woven into the fabric of civilization, cybersecurity becomes a global mandate—an investment in the future of economies, societies, and individuals. The insights laid bare in the WEF’s Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025 highlight a pivotal truth: leading organizations see cybersecurity not as a cost, but as a catalyst for growth and trust.
SAFE Can Help
SAFE can help organizations monitor and manage cyber resilience on a continuous basis. By aligning security findings with business impact, SAFE can empower leaders to make continuous, informed, data-driven decisions that protect the bottom line!
Why a continuous approach to cyber resilience matters:
- Ecosystem Transparency: Provide end-to-end visibility for your cybersecurity posture, across your entire attack surface, including supply chain partners.
- Quantified Risk Insights: Turn your cyber risks into dollars and cents to support decisions that make sense business-wise!!
- Proactive Resilience: Empower your teams to prioritize, align, and allocate resources to reduce loss exposure and stay one step ahead of the game!