ACE Your TPRM Program Compliance with ISO 27001, SOC2, and NIST CSF Using SAFE’s Agentic AI
Automate the entire vendor risk management lifecycle – with continuous compliance
By SAFE Threat Research Team
Traditional TPRM is heavily reliant on manual triggers, stakeholder back-and-forth, and sequential decision-making. From intake to offboarding, each handoff introduces time delays and inconsistent risk visibility. But AI is now re-engineering this workflow end-to-end.
SAFE’s TPRM platform is purpose-built to modernize vendor risk-management workflows by integrating artificial intelligence, automation, and compliance-by-design into every phase of the third-party lifecycle. SAFE eliminates manual bottlenecks, accelerates vendor onboarding, and ensures continuous compliance with global standards, enabling organizations to scale their TPRM programs efficiently.
The platform delivers an intelligent, compliance-aligned architecture that automates and orchestrates the full vendor lifecycle. Powered by embedded AI agents, it dynamically adapts to business context, vendor criticality, and evolving regulatory requirements. SAFE not only accelerates assessments but ensures that all decisions are risk-informed and framework-aligned.
Mapping SAFE’s TPRM Capabilities to Leading Frameworks
ISO 27001:2022
| Control Reference | Control Requirement | How SAFE Supports |
|---|---|---|
| A.5.19 | Processes and procedures shall be defined and implemented to manage the information security risks associated with the use of the supplier’s products or services. | SAFE automates supplier onboarding and risk-tiering, ensuring controls are applied based on business criticality. |
| A.5.20 | Relevant information security requirements shall be established and agreed with each supplier based on the type of supplier relationship | SAFE enables tailored control sets and AI-driven contract reviews to verify that key security clauses are in place. |
| A.5.21 | Processes and procedures shall be defined and implemented to manage the information security risks associated with the ICT products and services supply chain. | SAFE supports ICT supply chain due diligence with vendor classification, scoped assessments, and continuous tracking. |
| A.5.22 | The organization shall regularly monitor, review, evaluate, and manage changes in supplier information security practices and service delivery | SAFE offers continuous monitoring, automated alerts, and real-time visibility into changes in vendor risk posture. |
NIST CSF 2.0
| Control Reference | Control Requirement | How SAFE Supports |
|---|---|---|
| GV.SC-03 | Cybersecurity supply chain risk management is integrated into cybersecurity and enterprise risk management, risk assessment, and improvement processes | SAFE aligns third-party risk insights with broader enterprise risk programs to support integrated assessments and decision-making. |
| GV.SC-04 | Suppliers are known and prioritized by criticality | SAFE auto-classifies vendors by criticality using business context, business resource, and data access. |
| GV.SC-05 | Requirements to address cybersecurity risks in supply chains are established, prioritized, and integrated into contracts and other types of agreements with suppliers and other relevant third parties | SAFE uses AI to analyze contracts and enables organizations to define, review, and track key cybersecurity requirements in these contracts. |
| GV.SC-06 | Planning and due diligence are performed to reduce risks before entering into formal supplier or other third-party relationships | SAFE facilitates automated due diligence through standardized intake forms, tiering, and assessment workflows before formal engagement. |
| GV.SC-07 | The risks posed by a supplier, their products and services, and other third parties are understood, recorded, prioritized, assessed, responded to, and monitored over the course of the relationship | SAFE provides a centralized system to track supplier risks, conduct assessments, and monitor changes over time. |
| GV.SC-08 | Relevant suppliers and other third parties are included in incident planning, response, and recovery activities | SAFE helps identify critical suppliers to help organizations document their roles in incident preparedness and response processes. |
| GV.SC-09 | Supply chain security practices are integrated into cybersecurity and enterprise risk management programs, and their performance is monitored throughout the technology product and service life cycle | SAFE ensures supplier performance is continuously monitored through multiple dashboards, such as the Best-Performing Supplier, the Worst-Performing Supplier, and the Riskiest Supplier. |
| GV.SC-10 | Cybersecurity supply chain risk management plans include provisions for activities that occur after the conclusion of a partnership or service agreement | SAFE enables structured offboarding processes, including the offboarding questionnaire, final risk reviews, and access deprovisioning. |
| ID.RA-10 | Critical suppliers are assessed prior to acquisition | SAFE enables early-stage assessments for suppliers identified as critical to reduce pre-engagement risk. |
AICPA SOC 2
| Control Reference | Control Requirement | How SAFE Supports? |
|---|---|---|
| CC 9.2 – Establishes Requirements for Vendor and Business Partner Engagements | The organization establishes specific requirements for a vendor and business partner engagement that includes:1. Scope of services and product specifications2. Roles and responsibilities3. Compliance requirements4. Service levels | SAFE captures structured engagement requirements through intake forms and risk-based questionnaires, ensuring all key parameters are defined. |
| CC 9.2 – Assesses Vendor and Business Partner Risks | The organization assesses, on a periodic basis, the risks that vendors and business partners (and those entities’ vendors and business partners) represent to the achievement of the organization’s objectives. | SAFE enables periodic risk reassessments and continuous monitoring to track changes in vendor posture or risk exposure. |
| CC 9.2 – Assigns Responsibility and Accountability for Managing Vendors and Business Partners | The organization assigns responsibility and accountability for the management of risks associated with vendors and business partners. | SAFE supports role-based workflows and accountability tracking across procurement, legal, security, and risk functions. |
| CC 9.2 – Establishes Exception Handling Procedures From Vendors and Business Partners | The organization establishes exception handling procedures for service or product issues related to vendors and business partners. | SAFE supports the Exceptions workflow and tracking of accepted residual risks. |
| CC 9.2 – Assesses Vendor and Business Partner Performance | The organization periodically assesses the performance of vendors and business partners. | SAFE enables performance reviews through SLA tracking and assessment scores. |
| CC 9.2 – Implements Procedures for Addressing Issues Identified During Vendor and Business Partner Assessments | The organization implements procedures for addressing issues identified with vendor and business partner relationships. | SAFE provides structured workflows to capture findings, assign corrective actions, and monitor issue closure. |
| CC 9.2 – Implements Procedures for Terminating Vendor and Business Partner Relationships | The organization implements procedures for terminating vendor and business partner relationships. | SAFE enables structured offboarding processes, including the offboarding questionnaire, final risk reviews, and access deprovisioning. |
| CC 9.2 – Obtains Confidentiality Commitments from Vendors and Business Partners | The organization obtains confidentiality commitments that are consistent with the organization’s confidentiality commitments and requirements from vendors and business partners who have access to confidential information. | SAFE enables tracking and review of confidentiality clauses as part of contract evaluation, with AI-assisted clause detection. |
| CC 9.2 – Assesses Compliance With Confidentiality Commitments of Vendors and Business Partners | On a periodic and as-needed basis, the organization assesses compliance by vendors and business partners with the organization’s confidentiality commitments and requirements. | SAFE supports periodic reviews, evidence collection, and audit trails to evaluate vendor adherence to confidentiality obligations. |
| CC 9.2 – Obtains Privacy Commitments from Vendors and Business Partners | The organization obtains privacy commitments, consistent with the organization’s privacy commitments and requirements, from vendors and business partners who have access to personal information. | SAFE ensures privacy-related clauses are reviewed during assessments and contracts, aligned with data classification and access. |
| CC 9.2 – Assesses Compliance with Privacy Commitments of Vendors and Business Partners | On a periodic and as-needed basis, the organization assesses compliance by vendors and business partners with the organization’s privacy commitments and requirements and takes corrective action as necessary. | SAFE enables privacy assessments, evidence collection, and corrective action tracking as part of periodic reviews. |
AI in Action: Accelerating the TPRM Compliance Management Lifecycle
While frameworks like ISO 27001, SOC 2, and NIST CSF define “what” must be done, SAFE defines “how” to do it efficiently with speed, scalability, and impact.
Here’s how SAFE TPRM transforms the flow and slashes effort and time at needed and specific stages:
1. Assessment Initiation
| Traditional Approach | SAFE TPRM’s AI-driven Approach |
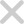
| Initiating a third-party risk assessment typically takes weeks. Business units must manually submit intake forms, and risk teams often struggle to extract relevant context. Vendor criticality is classified subjectively, and control set selection is inconsistent, leading to delays and scope misalignment. | Auto outside-in assessment initiation using public risk indicatorsBusiness context extracted from intake forms using AIAI classifies vendor criticality based on relationship and dataAuto-triggers questionnaire from the dynamic library based on the tierEstimated time reduction: 60–70% |
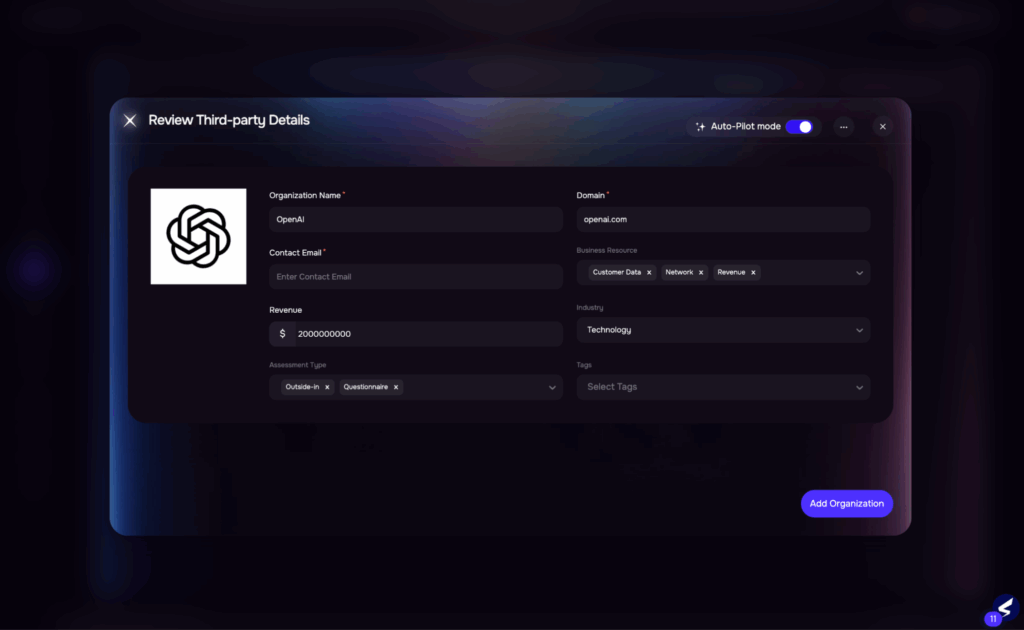
Image 1: Vendor Onboarding
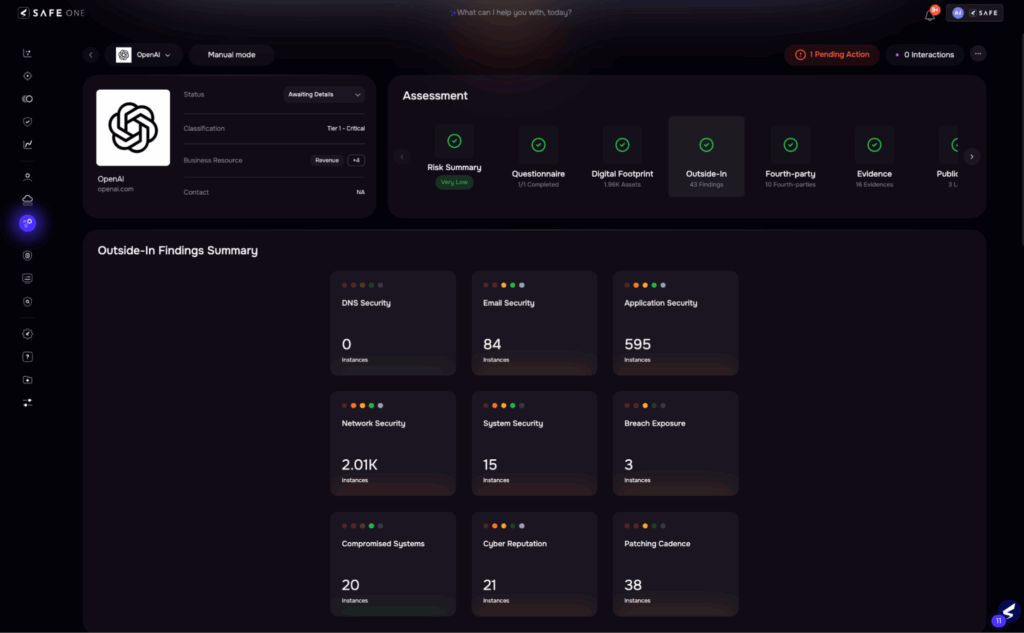
Image 2: Automated Inside-out Assessment
2. Risk Tiering and Control Selection
| Traditional Approach | SAFE TPRM’s AI-driven Approach |
| Control sets are often chosen manually with little standardization. Risk tiering is based on limited inputs and lacks business-contextual alignment. As a result, controls are either over-engineered for low-risk vendors or insufficient for high-risk ones, increasing both workload and risk exposure. | Auto-assignment of vendor tiers using business data and impact modellingAI recommends control sets aligned to risk tier and compliance needsTiering logic adjusts dynamically as vendor context evolvesEstimated effort reduction: 50–60% |
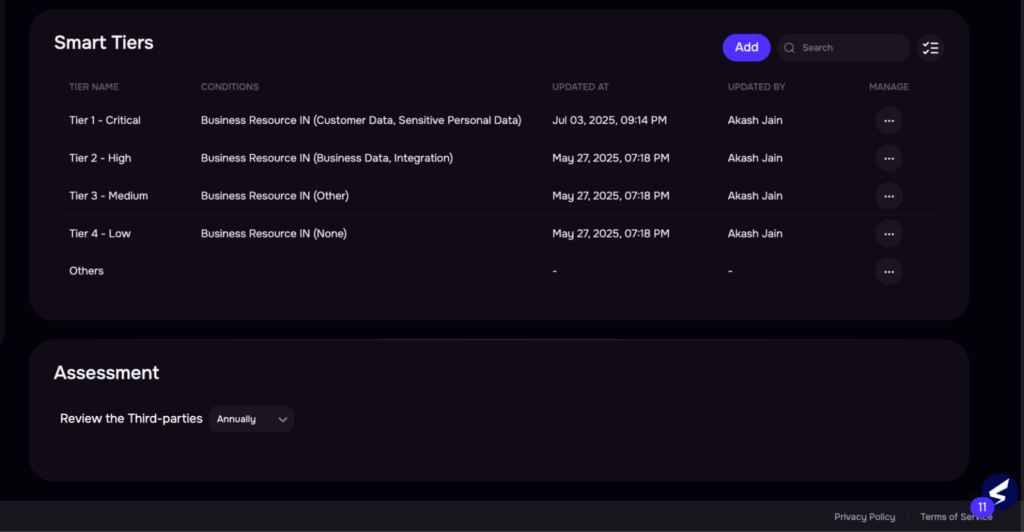
Image 3: Smart Tiering
3. Vendor Questionnaire Evaluation
| Traditional Approach | SAFE TPRM’s AI-driven Approach |
| Vendors are sent lengthy questionnaires with multiple follow-ups over email. Responses are often incomplete or vague. Risk teams manually validate responses and supporting documents, leading to long cycles and inconsistent reviews. | Auto-populates known answers from past engagements or data feedsNLP parses and validates uploaded documentsIntelligent follow-up prompts based on gaps or red flagsEstimated time reduction: 60–70% |
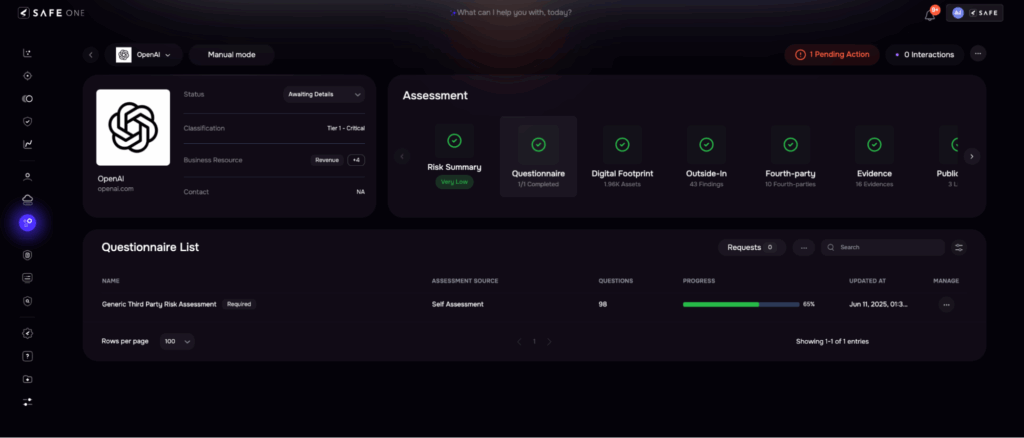
Image 4: Questionnaire Assessment
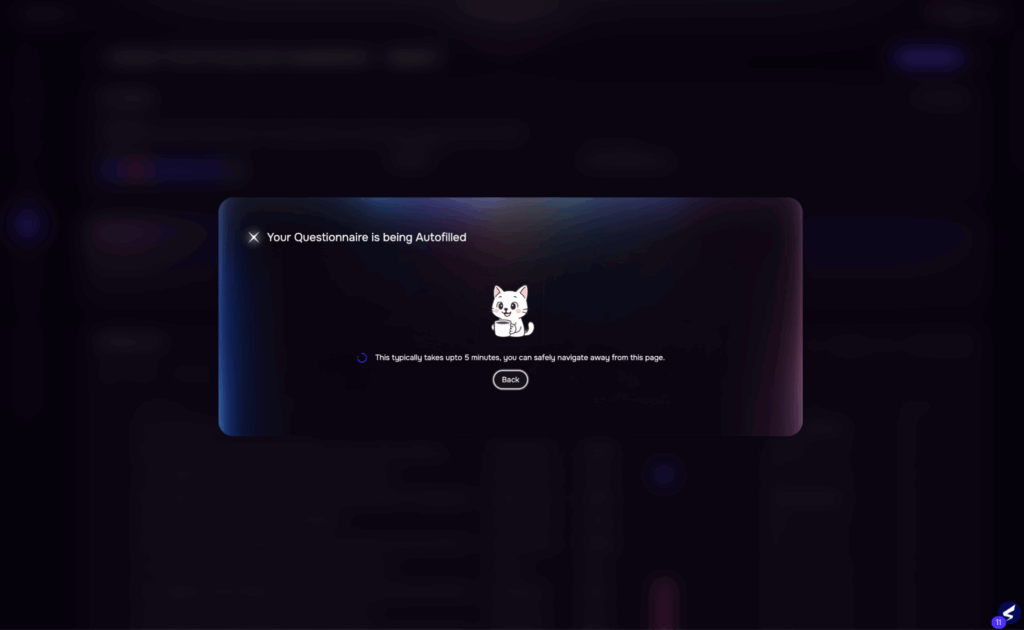
Image 5: AI Analysis on Compliance Reports
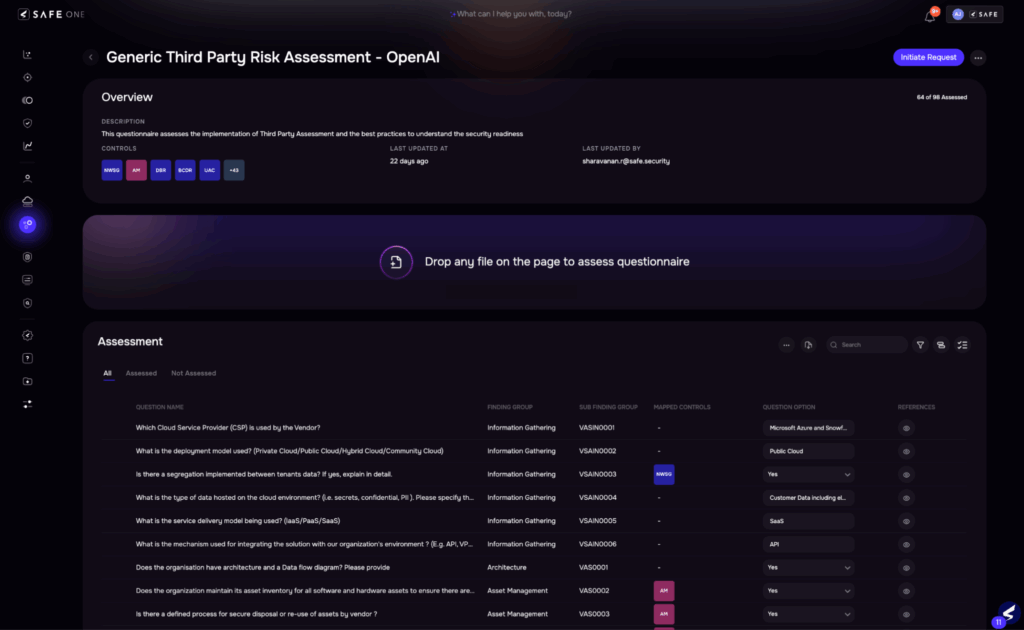
Image 6: AI-generated output
4. Document & Evidence Validation
| Traditional Approach | SAFE TPRM’s AI-driven Approach |
| Security policies, certifications, and audit reports are reviewed manually. Analysts spend time verifying authenticity and relevance, often lacking tools to interpret technical content. This results in long review cycles and possible oversights. | AI reads and validates submitted evidence against expected controlsFlag inconsistencies or missing elements automaticallyPulls contextual metadata to assess relevanceEstimated effort reduction: 50–60% |
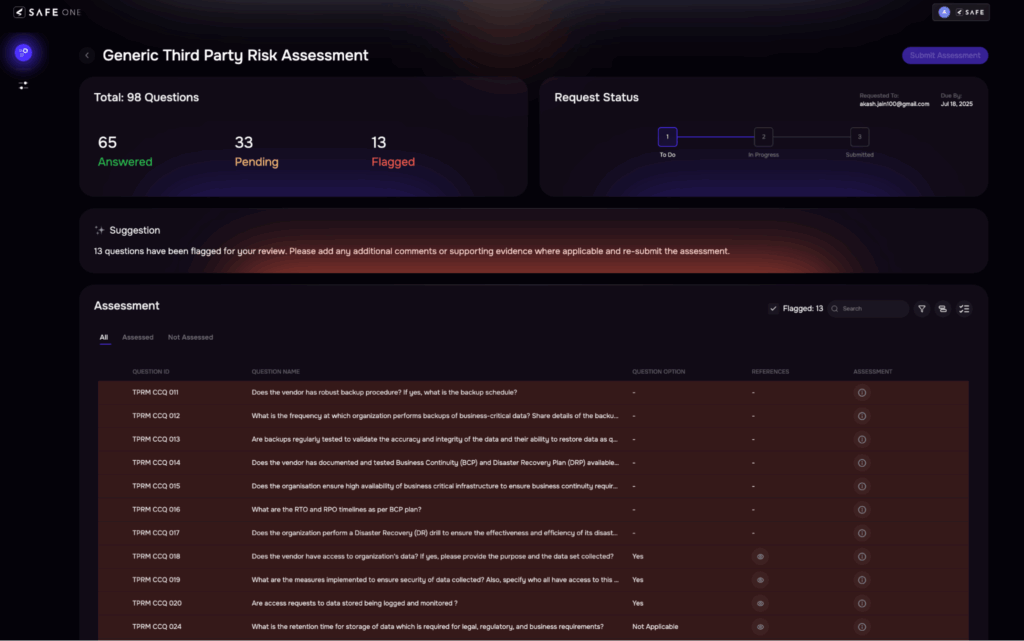
Image 7: Automatic Flagging
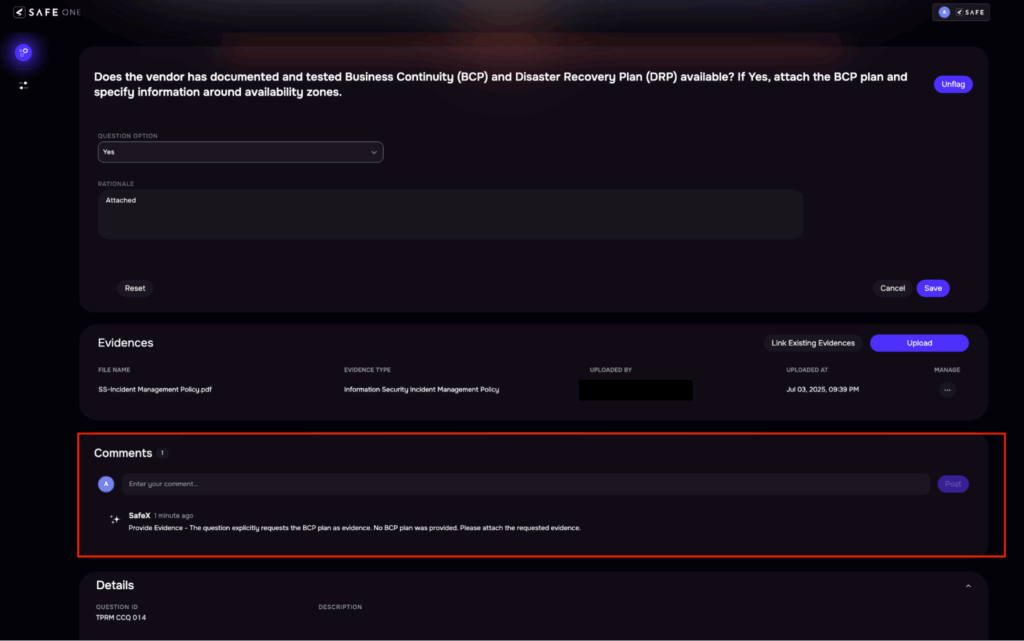
Image 8: AI Alerts for wrong evidence
5. Contract Evaluation
| Traditional Approach | SAFE TPRM’s AI-driven Approach |
| Contract review is handled by legal teams who manually check for risk clauses like indemnity, liability, SLAs, and data privacy terms. Negotiation loops are slow, and risk teams often lack visibility into these changes. | AI scans contracts for key risk clauses (security, privacy, liability, penalties, etc.) and provides suggestions for enhancementsReduce manual review efforts of LegalSuggests risk-aligned terms based on vendor risk profileEstimated time reduction: ~40–50%, with improved control enforcement |
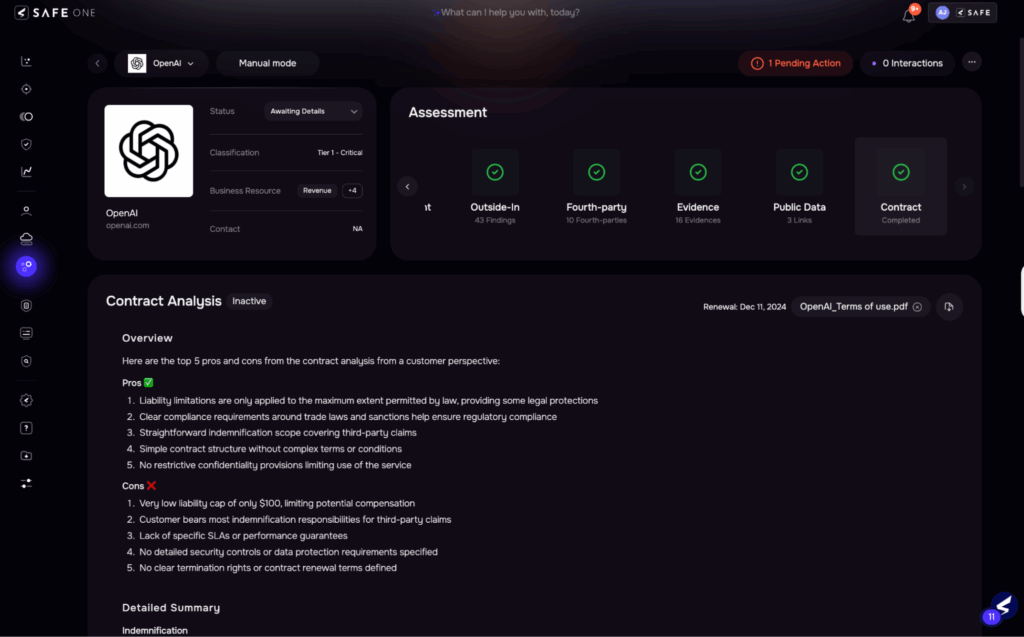
Image 9 Contract Analysis
6. Continuous Monitoring
| Traditional Approach | SAFE TPRM’s AI-driven Approach |
| Monitoring is reactive and periodic, often limited to annual reassessments. Emerging risks, SLA violations, or regulatory changes go unnoticed until it’s too late. Vendor transparency is also minimal post-onboarding. | Real-time monitoring via AI agentsAuto-alerts on breaches, SLA violations, and risk posture changesContinuous evidence collection from public sourcesEstimated time reduction: ~60% and faster risk mitigation |
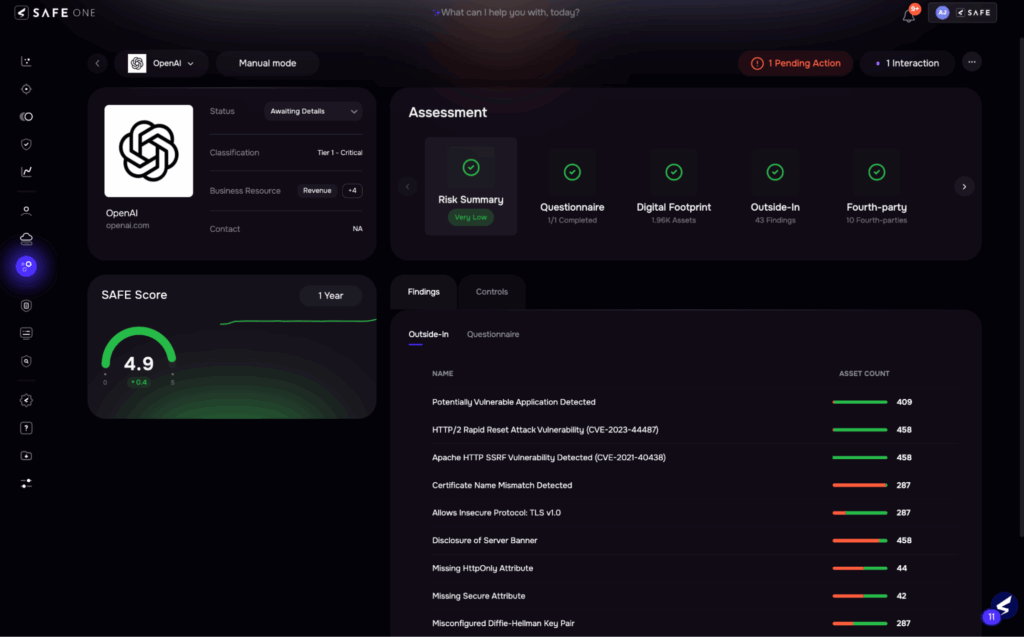
Image 10: Continuous Monitoring
Conclusion
As third-party ecosystems grow more complex and the risk landscape evolves faster than ever, traditional, manual TPRM approaches are no longer sustainable. Artificial Intelligence is not just a value-add; it’s a necessity for organizations seeking to scale their risk programs, respond in real-time, and ensure compliance with confidence.
SAFE helps organizations meet compliance requirements and redefine the TPRM experience. It empowers teams to focus on strategic decision-making rather than administrative tasks and enables a proactive, real-time approach to managing third-party risk.
By embedding intelligence into every phase of the vendor lifecycle, SAFE enables faster onboarding, smarter assessments, and continuous monitoring without overwhelming internal teams. It transforms TPRM from a reactive, checkbox-driven process into a proactive, insight-led strategy.
Are you curious about how SAFE can transform your TPRM program?
Watch TPRM In-action,Test Drive Yourself, or Book a live demo.