Benchmarking Your Cybersecurity Program in 2026
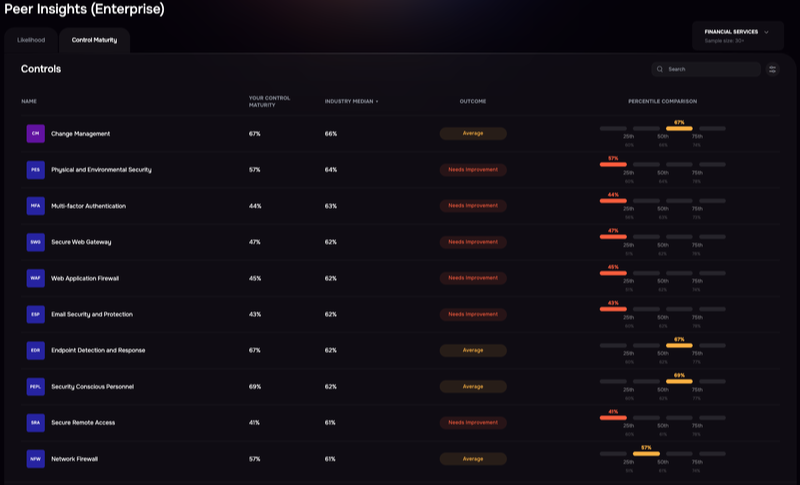
Benchmarking against peers with the SAFE One platform
Security leaders face an impossible question from their boards: “Are we secure enough?” Without benchmarking, the answer is pure guesswork—an assertion that security spending is working with no evidence to back it up.
Cybersecurity benchmarking compares your organization’s security posture against industry standards, peer organizations, or best practices to identify gaps and measure performance in concrete, defensible terms. This guide covers what benchmarking actually measures, which metrics matter most, how to implement a benchmarking program that scales, and how to translate technical security data into the financial risk language that executives and boards understand.
What Is Cybersecurity Benchmarking
Cybersecurity benchmarking is the practice of comparing your organization’s security posture against industry standards, peer organizations, or best practices to identify gaps and measure performance. It transforms abstract security concepts into measurable data points that show where you stand and where improvement is needed. Think of it as taking your security program’s vital signs and comparing them to what healthy looks like in your industry.
The process typically falls into three categories. Standards-based benchmarking compares your program against established frameworks like NIST CSF, CIS Controls, or ISO 27001. Peer benchmarking measures your security performance against similar organizations in your industry. Internal benchmarking tracks your own improvements over time, showing whether your investments are actually moving the needle.
When you benchmark, you’re establishing your baseline security posture—your current level of security maturity—and assessing how well your security controls (the technical and procedural safeguards protecting your assets) are actually working.
Why Benchmark Your Security Program
Security leaders face a persistent challenge: proving program effectiveness to boards and executives who speak the language of business risk, not technical vulnerabilities. Benchmarking provides the translation layer between these two worlds.
Here’s what benchmarking actually delivers:
- Quantified risk in business terms: Transform technical exposure into financial impact that resonates with CFOs and board members
- Investment prioritization based on gaps: Identify which controls deliver the most risk reduction per dollar spent
- Compliance readiness: Show auditors and regulators measurable progress against specific requirements
- Peer comparison: Understand whether your security maturity matches, exceeds, or lags behind industry standards
The practice also addresses mounting regulatory pressure. SEC cybersecurity disclosure rules and NYDFS requirements demand clear evidence of risk management, not just assertions that you’re “doing security.” Without benchmarking, you’re asking leadership to trust that security spending is working without providing any evidence.
Key Metrics and Security Benchmarks to Track
Effective benchmarking requires selecting metrics that are measurable, actionable, and tied to actual business risk. The following five categories provide visibility into security program performance without drowning in noise.
1. Incident Response Timelines
Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) measures how long it takes to identify that a breach has occurred. Mean Time to Respond (MTTR) measures how long it takes to contain and remediate the threat once detected. These two metrics reveal whether your security operations are reactive or proactive.
Industry leaders detect breaches in hours rather than days or months. The difference between detecting a breach in 24 hours versus 200 days can mean millions of dollars in prevented losses, not to mention the regulatory and reputational impact.
2. Vulnerability Management And Patching Cadence
Patching cadence tracks the percentage of critical vulnerabilities patched within 7, 14, or 30 days. This metric indicates whether your vulnerability management program is keeping pace with threat actors or falling behind.
Track vulnerability age (average time vulnerabilities remain unpatched), exposure window (time between disclosure and patch deployment), and remediation backlog by severity. Prioritize based on exploitability, business criticality, and existing control coverage rather than chasing CVSS scores alone. A critical vulnerability in an internet-facing system with no compensating controls demands faster action than an equally severe flaw in an isolated development environment.
3. Endpoint And Cloud Security Coverage
Coverage metrics measure how comprehensively security controls protect your assets. Gaps in coverage create exploitable blind spots—unprotected endpoints, misconfigured cloud storage, or administrative accounts without MFA become the paths adversaries take.
Track endpoint protection coverage (percentage of devices with EDR or antivirus deployed and updated), cloud security posture (percentage of cloud workloads with proper configurations and monitoring), MFA adoption rates, and privileged access management coverage.
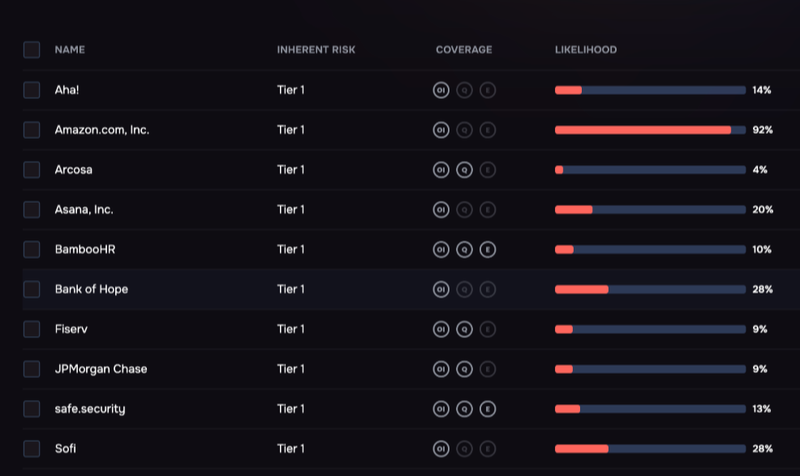
Tiering vendors by risk, SAFE One platform
4. Third-Party Risk Assessments
Supply chain attacks have made vendor cybersecurity posture a board-level concern. Traditional TPRM relies on manual questionnaires that don’t scale and provide only point-in-time snapshots. Modern approaches use automation and continuous monitoring to track vendor risk in real time.
Track vendor assessment completion rates, time to address critical findings in vendor assessments, continuous monitoring coverage, and vendor security scoring distribution across risk tiers. SAFE TPRM uses Agentic AI to autonomously assess and monitor vendors based on actual cybersecurity risk and potential financial loss rather than static ratings, reducing manual effort while increasing coverage.
5. Awareness and Training Metrics
Human behavior remains a leading breach cause. Track training completion rates, phishing simulation click-through rates, reporting rates for suspicious activities, and time to behavior change.
Declining click-through rates and increasing reporting rates indicate program maturity. If your phishing simulation click rate drops from 15% to 3% over six months while reporting increases, your training is working.
Implementing Cyber Security Benchmarking In Your Organization
Organizations struggle with fragmented security data scattered across dozens of tools. A structured five-step approach makes benchmarking manageable.
1. Identify Relevant Frameworks or Standards
Select benchmarking frameworks based on your industry, regulatory requirements, and organizational maturity. Different frameworks serve different purposes.
| Framework | Best For | Key Focus Areas |
| NIST Cybersecurity Framework | Broad applicability across industries | Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, Recover |
| CIS Controls | Tactical implementation guidance | Prioritized security actions |
| ISO 27001 | Compliance and certification | Information security management systems |
| MITRE ATT&CK | Threat-informed defense | Adversary tactics and techniques |
| FAIR | Risk quantification | Financial impact of cyber risk |
Many organizations layer frameworks—NIST for structure, CIS for implementation, FAIR for financial quantification to support business decision-making This combination provides both strategic direction and tactical guidance.
2. Map Security Controls to Benchmark Criteria
Mapping documents which security controls address specific framework requirements. Inventory existing security controls and tools, then align each control to framework requirements. Your EDR tool might address multiple NIST CSF subcategories. Identify coverage gaps where no control exists, then assess control effectiveness rather than merely checking for presence.
SAFE CRQ uses the FAIR-CAM (Controls Assessment Model) to automatically calculate control effectiveness across the enterprise, eliminating manual mapping effort. Manual approaches are time-intensive and quickly become outdated as tools and configurations change.
3. Gather and Normalize Data
Security data lives in 50+ disparate tools—SIEM, vulnerability scanners, EDR, firewalls, cloud security platforms—each with unique data formats. Integration via APIs, normalization into consistent schemas, data quality validation, and continuous feeds rather than point-in-time snapshots are essential.
Continuous monitoring provides real-time visibility into changing risk, unlike annual assessments that are outdated the moment they’re complete. Platforms like SAFE aggregate data from 100+ security tools automatically, eliminating manual collection and ensuring consistency.
4. Analyze Gaps and Prioritize Treatments
Gap analysis identifies where your security posture falls short of benchmark targets, but not all gaps are equally important. Risk-based prioritization focuses on gaps with the highest potential financial impact. Exploitability assessment prioritizes vulnerabilities and controls that adversaries actively target. Cost-benefit analysis calculates expected risk reduction per dollar invested.
Cyber Risk Quantification (CRQ) translates security gaps into dollar-denominated risk exposure. SAFE CRQ uses FAIR methodology to quantify risk in financial terms, answering which actions reduce the most financial risk at the lowest cost.
5. Communicate Results to Stakeholders
Benchmarking data requires translation into language that resonates with different audiences. Boards and executives need financial risk metrics, peer comparisons, compliance status, and ROI of security investments. Auditors and regulators want framework alignment, control maturity scores, and remediation timelines. Security teams require technical gap analysis, remediation priorities, and tool effectiveness metrics.
SAFE enables board-ready reporting aligned with SEC and NYDFS requirements, translating technical telemetry into business language that executives actually understand.
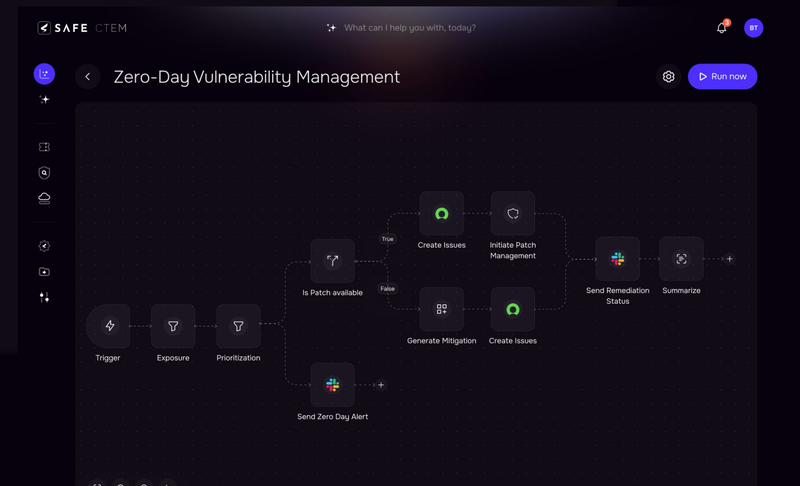
Realtime vulnerability assessment with SAFE TPRM
Leveraging Real Time and Continuous Cybersecurity Benchmarking
Traditional annual benchmarking provides only stale snapshots while risk changes daily as new vulnerabilities emerge and configurations drift. Annual assessments can’t scale to modern cloud environments where infrastructure changes hourly.
Continuous benchmarking delivers real-time visibility into current risk posture, automated detection of configuration drift and emerging exposures, granular trend analysis tracking security improvements, and event-driven alerts when benchmarks fall below thresholds. Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) unifies vulnerability data, prioritizes based on risk, and automates remediation workflows.
SAFE CTEM connects with leading tools including Tenable, Qualys, Rapid7, Wiz, and Prisma Cloud to provide unified, continuous exposure visibility. This approach replaces periodic vulnerability scans with always-on monitoring that reflects your actual, current security posture.
Incorporating Financial Risk Quantification in Your Security Benchmark
Traditional benchmarking shows compliance or maturity scores but doesn’t answer the critical question: “How much risk do we have?” in financial terms that business leaders understand. financial terms that business leaders understand. Cyber Risk Quantification (CRQ) expresses cyber risk in dollars using probabilistic models based on threat likelihood and potential impact.
CRQ measures loss exposure (probable financial impact of cyber events including breach costs, business interruption, and regulatory fines), Annualized Loss Expectancy (expected losses over a year), and risk reduction ROI (financial value of security investments). The FAIR (Factor Analysis of Information Risk) standard provides the industry framework for quantifying cyber risk.
Financial benchmarking transforms security conversations. Executives understand risk in the same language as market risk, credit risk, and operational risk. Boards can compare cyber risk exposure to risk appetite and tolerance. Security investments can be prioritized based on expected financial return rather than subjective judgment.
SAFE CRQ uses FAIR methodology to automatically calculate enterprise-wide risk in dollars, aggregating data from 100+ security tools and continuously monitoring exposure. This enables board-ready risk reporting that demonstrates security program value in business terms.
Accelerating Resilience with Future-Ready Security Benchmarks
Cybersecurity benchmarking is evolving from compliance-driven exercises to strategic business capabilities. The future includes autonomous risk management with AI-powered systems that continuously assess, prioritize, and remediate risk without manual intervention.
Agentic AI transforms benchmarking by automating data collection, analysis, gap identification, and reporting—enabling security teams to manage risk at scale without adding headcount. The SAFE Platform provides Autonomous Cyber Risk Management powered by 25+ specialized AI agents that handle continuous benchmarking, quantification, and prioritization across enterprise, third-party, and exposure domains.
Organizations using SAFE transform cybersecurity from a compliance function into a strategic business accelerator. They quantify risk in financial terms, optimize investments based on ROI, automate continuous risk monitoring across their enterprise and supply chain, demonstrate defensibility to auditors and regulators, and prove security value to leadership and boards.
See how SAFE can transform your cybersecurity benchmarking program. Schedule a demo to experience Autonomous Cyber Risk Management.
FAQs About Cybersecurity Benchmarking
How can organizations automate cybersecurity benchmarking without increasing staff?
Platforms with AI-powered automation continuously collect data from security tools, calculate benchmark metrics, and generate reports without manual effort, enabling teams to scale risk management programs without adding headcount.
What should organizations do if they use multiple security frameworks for benchmarking?
Map overlapping controls across frameworks to avoid duplication, then use a unified platform that simultaneously tracks compliance and maturity across multiple standards while providing a consolidated risk view.
See how the SAFE platform benchmarks your cybersecurity program – Schedule a demo now.


