Aligning IT and Cybersecurity: The Missing Piece in Business Alignment
Break through the silos by quantifying cyber risk in business terms
By Wes Hendren
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses are increasingly recognizing that aligning IT and cybersecurity is the missing piece in achieving comprehensive business alignment. While many organizations have made strides in integrating IT with business objectives, cybersecurity and information technology often remain siloed, leading to gaps in risk management and strategic execution.

The Evolution of Business Alignment: IT’s Role and Limitations
Over the past few years, Chief Information Officers (CIOs) and Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) have transformed from technical caretakers to strategic business enablers. By adopting Technology Business Management (TBM) practices, these executives have begun managing technological investments based on business value rather than mere technical metrics.
Core Tenets of TBM Enhancing Business Alignment
- Positioning for Value: Delivering IT services that enhance business capabilities.
- Cost Transparency: Providing clear insights into IT costs and consumption.
- Value for Money: Ensuring cost-effectiveness of IT services.
- Strategic Alignment: Aligning IT budgets with business imperatives.
- Value Conversations: Facilitating discussions that optimize IT portfolios for maximum business value.
Despite these advancements, a critical component remains underrepresented in the alignment process: cybersecurity and information technology.
Cybersecurity: The Missing Piece in Business Alignment
Cybersecurity risks have escalated, impacting not just information technology systems but entire business operations and bottom lines. Traditional risk assessments often rely on qualitative metrics that fail to resonate with business leaders, leaving key questions unanswered:
- Are we investing appropriately in cybersecurity?
- Are we focusing on the most significant risks?
- How do cyber risks affect our financial performance?
This disconnect indicates that without integrating cybersecurity into the business alignment framework, organizations expose themselves to unmanaged risks that can derail strategic objectives.
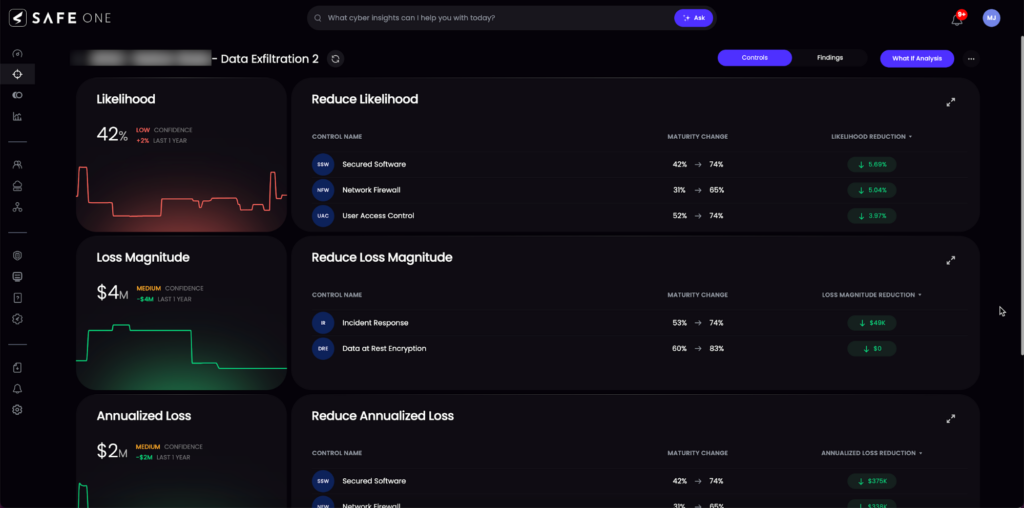
Introducing FAIR: Quantifying Cyber Risk to Complete the Alignment
The Factor Analysis of Information Risk (FAIR) model offers a solution by quantifying cyber risks in financial terms. By translating technical vulnerabilities into business impacts, FAIR enables organizations to integrate cybersecurity into their overall business alignment efforts.
How FAIR Completes the Alignment
- Articulates Cyber Risk in Business Terms: Communicates risks in dollars and cents, making them tangible for all stakeholders.
- Prioritizes Mitigation Efforts: Focuses on risks that have the most significant business impact.
- Calculates ROI on Cybersecurity Investments: Assesses the effectiveness of cybersecurity spending.
- Enhances Regulatory Compliance: Addresses compliance requirements by prioritizing critical risks.
- Integrates with Existing Frameworks: Adds an economic dimension to standards like NIST CSF and ISO 27001.
Learn how SAFE solves for automating FAIR.
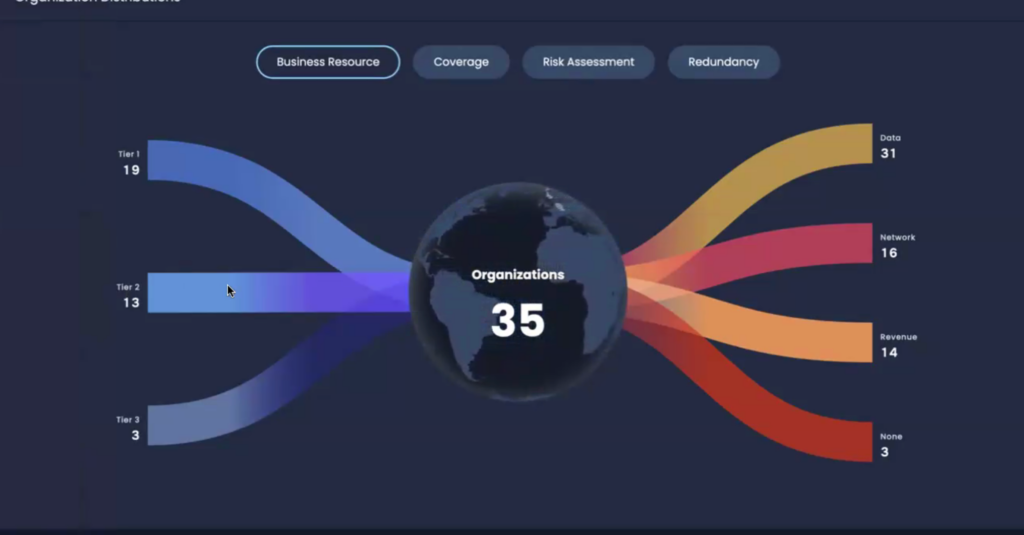
Unifying First and Third-Party Cyber Risk Management: The Platform for Complete Alignment
At SAFE, we understand that aligning IT and cybersecurity requires a unified approach to risk management. By consolidating First-Party and Third-Party Risk Management on a single platform, organizations can:
- Achieve Comprehensive Risk Visibility: Understand all internal and external cyber risks affecting the business.
- Streamline Risk Assessments: Apply consistent metrics across the organization for accurate evaluations.
- Improve Stakeholder Communication: Present risks in financial terms that resonate with all business leaders.
- Enhance Decision-Making: Enable data-driven strategies that align cybersecurity efforts with business objectives.
Stakeholder Benefits: Completing the Alignment Puzzle
CEOs: Informed Decision-Making and Growth Enablement
- Strategic Clarity: Balance opportunities and risks for sustainable growth.
- Governance Assurance: Demonstrate proactive management to stakeholders and regulators.
- Risk-Aware Culture: Foster an organization-wide understanding of cyber risks.
CFOs: Financial Stewardship and Investment Optimization
- Budget Allocation: Prioritize investments based on potential financial impacts.
- Financial Reporting: Integrate cyber risk metrics into financial disclosures.
- Cost Savings: Avoid unnecessary expenses by focusing on significant risks.
Chief Counsel: Legal Risk Mitigation and Compliance
- Liability Reduction: Identify and address vulnerabilities proactively.
- Regulatory Alignment: Ensure compliance with evolving cybersecurity laws.
- Contractual Security: Strengthen agreements with third parties to mitigate risks.
CIOs: Strategic Leadership and Efficient Operations
- Holistic Oversight: Manage IT and cybersecurity cohesively for better alignment.
- Resource Optimization: Allocate budgets effectively by understanding the financial impact of risks.
- Enhanced Influence: Lead strategic discussions with quantified risk data.
CISOs: Effective Risk Management and Communication
- Prioritized Action: Focus on mitigating risks that affect business objectives.
- Executive Engagement: Communicate effectively with leadership using financial metrics.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamline cybersecurity efforts through unified risk management.
Real-World Impact: Organizations Bridging the Alignment Gap
Leading companies like ADP, GSK, and Molina Healthcare have recognized that aligning information technology and cybersecurity is essential for complete business alignment. By integrating TBM and FAIR, and unifying First and Third-Party Cyber Risk Management, they have:
- Strengthened Risk Posture: Achieved a comprehensive understanding of cyber risks.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Improved communication between technical teams and business leaders.
- Driven Business Value: Optimized investments leading to better financial performance and competitive advantage.
Conclusion: Bridging the Alignment Gap with SAFE
Aligning IT and cybersecurity is the missing piece in achieving full business alignment. By adopting quantitative risk models like FAIR and unifying First and Third-Party Cyber Risk Management on a single platform, organizations can fill this gap. This integration not only enhances risk management but also empowers all stakeholders to contribute to strategic objectives effectively.
At SAFE, we’re dedicated to helping organizations bridge this gap. Our unified platform enables you to align cybersecurity with business goals, ensuring that IT and cybersecurity are no longer siloed but are integral parts of your business strategy. Contact us for a 30-minute demo.


