Why Zero-Trust Matters in Third-Party Risk Management
Would you agree that setting up fire alarms in your apartment is necessary before advocating for fire prevention measures in the community? Similarly, isn’t installing security cameras at home necessary before initiating a neighborhood crime prevention group?
If you answered “yes” to the above, why does our approach to third-party risk differ? Why do we not include visibility into how well first-party controls are configured, which can impact third-party breaches? This is where zero-trust principles come into play — emphasizing that no entity, whether inside or outside the network, should be trusted by default. Let’s explore why zero-trust is imperative for third-party security.
The Impact of Third-Party Breaches
Third-party relationships are fundamental to business operations. For an average enterprise, this means dealing with thousands of third parties, each posing a potential security risk. According to Forrester, 60% of security incidents result from issues with third parties, and Gartner predicts that 45% of organizations worldwide will experience software supply chain attacks by 2025.
Given this landscape, traditional TPRM solutions may fall short of providing the necessary visibility and control to mitigate these risks effectively. This is where zero-trust principles come into play.
The Ticketmaster Breach
Take the Ticketmaster breach — the latest in a long line of third-party breaches. Here are some alarming statistics:
- Hackers allegedly stole data from Ticketmaster and other customers of cloud storage firm Snowflake by first breaching a third-party contractor.
- 165 customer accounts, including those of Ticketmaster, Santander, Lending Tree, and Advance Auto Parts, were potentially compromised.
- Access through third-party contractors was identified as the initial entry point. EPAM Systems was one of the contractors that hackers exploited unencrypted usernames and passwords stored on an employee’s machine.
- Lack of multifactor authentication (MFA) on Snowflake accounts added to the vulnerability, prompting the company to implement MFA post-breach.
This breach underscores the dire need for real-time visibility into how first-party controls affect third-party risks. Would such visibility have made a difference? Absolutely.
What is Zero-Trust TPRM?
The traditional security strategy emphasizes perimeter defenses, where a robust password is deemed sufficient for granting access. Upon breaching the network perimeter, users are typically classified as “trusted” and granted extensive resource access. However, relying solely on perimeter-based access fails to deter malicious actors originating from within the perimeter.
The zero-trust model operates under the principle of “never trust, always verify.” In the context of third party cyber risk management, this means not inherently trusting any third party, regardless of their network position or past interactions. Instead, continuously verify third-party controls to ensure they meet stringent security standards before granting access to sensitive data or critical infrastructure.
It means shifting from merely reducing the likelihood of third-party breaches to strengthening internal controls to reduce the likelihood and impact of such incidents. By incorporating zero-trust principles, a TPRM solution continuously verifies third-party controls, ensuring they meet stringent security standards before granting access to sensitive data or critical infrastructure.
Key Features of Zero-Trust Third-Party Controls
- Continuous Verification
The platform consistently verifies the security standards of all third parties, ensuring they meet strict criteria before any data access is granted. This includes real-time scans of native controls to detect any changes or new vulnerabilities. - Internal Resiliency Controls
Provides insights into how first-party controls defend against potential third-party risks. This helps assess current security measures undertaken by the enterprise and adjust them to address specific vulnerabilities. - Liability Transfer
By enforcing strict security measures and ensuring third parties comply, organizations can transfer some liability, protecting themselves from the potential repercussions of third-party breaches. - Insight-Driven Resource Allocation
With a clear understanding of the effectiveness of existing security controls, organizations can strategically allocate resources. This enables them to bolster defenses in areas most susceptible to risks, ensuring cybersecurity investments are effective and cost-efficient.Zero-trust strategy in third party cyber risk management ensures minimal vendor access for maximum security. Vendors and internal users are strictly controlled with technology like multi-factor authentication and endpoint security. Implementing this requires Vendor Privileged Access Management (VPAM) and comprehensive audits to prevent breaches. Organizations must adopt zero-trust capabilities to protect against cyberattacks involving credential misuse.Within third party cyber risk management, the adoption of a zero-trust strategy typically revolves around establishing robust controls to restrict vendor access solely to the essential resources required for their tasks without excess privileges.
Under the zero-trust framework, vendors and internal users are effectively segregated with stringent oversight mechanisms, regardless of their access points or methods.
Managing third-party trust can pose challenges due to the dynamic nature of vendor interactions across diverse locations. Hence, zero-trust leverages technologies like multi-factor authentication, endpoint security, and contemporary cloud management to authenticate and uphold system integrity. Its successful implementation involves two critical elements:
- Vendor Privileged Access Management (VPAM): VPAM technology ensures precise least-privilege restrictions during vendor user onboarding while swiftly revoking access when service agreements conclude.
- Thorough Auditing: Continuous and extensive audits post-onboarding are vital to monitor vendor users’ adherence to restrictions, promptly flagging any unauthorized activities.
Organizations are urged to embed zero-trust capabilities, especially when granting external entities access to their internal systems. Notably, over 80% of cyber incidents involve credential misuse, as reported by Crowdstrike.
How SAFE TPRM Can Help
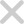
Zero-trust principles drive SAFE TPRM, providing real-time visibility into an enterprise’s internal resiliency controls for its third parties. It categorizes enterprise controls into likelihood reduction and business continuity controls to enhance control effectiveness in minimizing third-party data breaches. These insights help businesses redistribute resources and improve their internal cyber risk resilience, minimizing the impact of potential breaches.
Navigate Risk Control Focus
Shift from merely trying to reduce the likelihood of third-party breaches to strengthening controls within your own scope to minimize both likelihood and potential loss. This approach ensures you’re not just reacting to threats but proactively managing them.
Third-Party Risk Exposure Likelihood Reduction
Third-party risk exposure likelihood reduction control consists of security gates implemented by the first-party organization to safeguard its network and data in case of a breach at a third party.
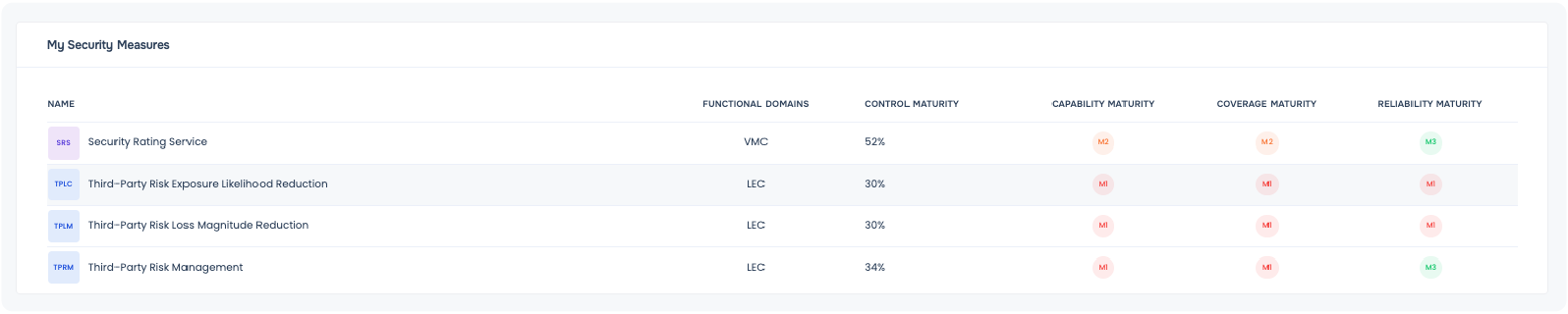
Third-Party Risk Loss Magnitude Reduction
Third-party risk loss reduction control consists of security monitoring capabilities implemented by the first-party organization to minimize the impact of a security incident at a third party. These security capabilities act as a layered defense.
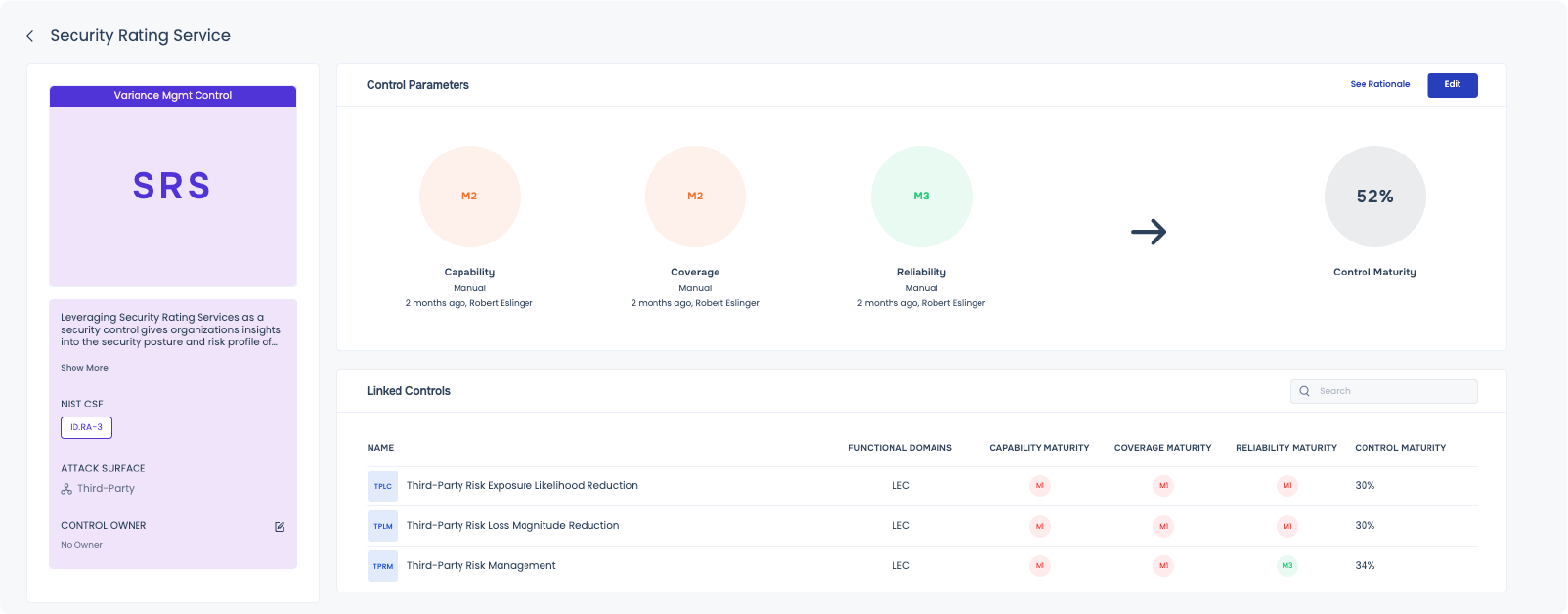
The zero-trust model embedded within SAFE TPRM ensures that all interactions with third parties are continuously scrutinized and controlled from initial access throughout their engagement. This constant monitoring and reassessment of third-party activities and their access privileges safeguard your organization’s sensitive data and systems from unauthorized access and potential threats.
Get a 5-step blueprint for transforming third party cyber risk management in this whitepaper. Read now.
Elevate Your Third-Party Risk Management Strategy With SAFE TPRM
The Ticketmaster breach is a cautionary tale illustrating the vulnerabilities inherent in traditional TPRM. Incorporating zero-trust principles into third party cyber risk management is not just a best practice; it is imperative for protecting your organization from the increasing threat of third-party breaches. SAFE TPRM empowers businesses to take a proactive stance, continuously verifying third-party controls and ensuring robust internal defenses.
It’s time to adopt a zero-trust approach to TPRM. Protect your enterprise by managing third-party risk effectively with SAFE TPRM.
Ready to strengthen your third party cyber risk management? Book a call with one of our experts to learn how SAFE TPRM can help you implement a more secure and efficient approach.